Synthesis and characterization of novel luminescent europium(iii) hybrid materials with a host based on titania–mesoporous silica or alumina–mesoporous silica†
Abstract
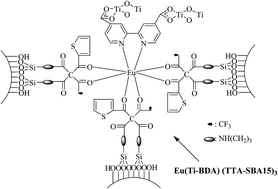
The luminescent mesoporous hybrids, Eu(M-BDA)2(TTA-SBA15)3 and Eu(M-BDA)2(TTA-MCM41)3 (M = Ti, Al), were obtained after the coordination reaction between Eu3+ ions and a functionalized organic ligand (TTA-SBA15 or TTA-MCM41 and M-BDA (M = Ti, Al)) followed by the hydrolysis cross-linking reaction. All the mesoporous hybrids were found to retain their highly ordered mesoporous structures and possessed good thermal stability characterized by FTIR, SAXRD, TEM, N2 adsorption–desorption curves, and TG analyses. Especially the photoluminescence behaviors (e.g., photoluminescent spectra, luminescence decay analysis, and 5D0 quantum efficiency) of the Eu3+ hybrid materials were investigated in detail. Results showed that SBA-15-type mesoporous hybrids Eu(M-BDA)2(TTA-SBA15)3, with larger pore sizes than the corresponding MCM-41-type hybrids Eu(M-BDA)2(TTA-SBA15)3, presented longer luminescent lifetimes and higher quantum efficiency than the latter because of spatial confinements of mesoporous matrix nanochannels. The Al–O based mesoporous hybrids also exhibited more excellent luminescent properties than the corresponding Ti–O based hybrids, suggesting that the Al–O host was more beneficial to Eu3+ ion luminescence than the Ti–O host. The quantum efficiency of Eu(Al-BDA)(TTA-SBA15)3 was high even up to 43.17%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...