Directed evolution of cyclic peptides for inhibition of autophagy†
Abstract
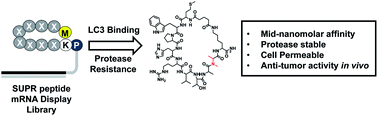
In recent decades it has become increasingly clear that induction of autophagy plays an important role in the development of treatment resistance and dormancy in many cancer types. Unfortunately, chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), two autophagy inhibitors in clinical trials, suffer from poor pharmacokinetics and high toxicity at therapeutic dosages. This has prompted intense interest in the development of targeted autophagy inhibitors to re-sensitize disease to treatment with minimal impact on normal tissue. We utilized Scanning Unnatural Protease Resistant (SUPR) mRNA display to develop macrocyclic peptides targeting the autophagy protein LC3. The resulting peptides bound LC3A and LC3B—two essential components of the autophagosome maturation machinery—with mid-nanomolar affinities and disrupted protein–protein interactions (PPIs) between LC3 and its binding partners in vitro. The most promising LC3-binding SUPR peptide accessed the cytosol at low micromolar concentrations as measured by chloroalkane penetration assay (CAPA) and inhibited starvation-mediated GFP-LC3 puncta formation in a concentration-dependent manner. LC3-binding SUPR peptides re-sensitized platinum-resistant ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin treatment and triggered accumulation of the adapter protein p62 suggesting decreased autophagic flux through successful disruption of LC3 PPIs in cell culture. In mouse models of metastatic ovarian cancer, treatment with LC3-binding SUPR peptides and carboplatin resulted in almost complete inhibition of tumor growth after four weeks of treatment. These results indicate that SUPR peptide mRNA display can be used to develop cell-penetrating macrocyclic peptides that target and disrupt the autophagic machinery in vitro and in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...