Phosphonopeptides containing free phosphonic groups: recent advances†
Abstract
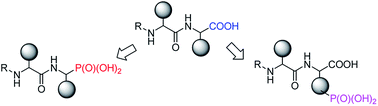
Phosphonopeptides are mimetics of peptides in which phosphonic acid or related (phosphinic, phosphonous etc.) group replaces either carboxylic acid group present at C-terminus, is located in the peptidyl side chain, or phosphonamidate or phosphinic acid mimics peptide bond. Acting as inhibitors of key enzymes related to variable pathological states they display interesting and useful physiologic activities with potential applications in medicine and agriculture. Since the synthesis and biological properties of peptides containing C-terminal diaryl phosphonates and those with phosphonic fragment replacing peptide bond were comprehensively reviewed, this review concentrate on peptides holding free, unsubstituted phosphonic acid moiety. There are two groups of such mimetics: (i) peptides in which aminophosphonic acid is located at C-terminus of the peptide chain with most of them (including antibiotics isolated from bacteria and fungi) exhibiting antimicrobial activity; (ii) non-hydrolysable analogues of phosphonoamino acids, which are useful tools to study physiologic effects of phosphorylations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...