Highly modulated supported triazolium-based ionic liquids: direct control of the electronic environment on Cu nanoparticles†
Abstract
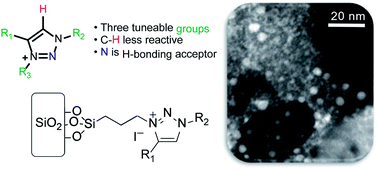
A series of new triazolium-based supported ionic liquids (SILPs), decorated with Cu NPs, were successfully prepared and applied to the N-arylation of aryl halides with anilines. The triazoles moieties were functionalised using copper-catalysed azide–alkyne cycloaddition. SILP surface characterisation showed a strong correlation between the triazolium cation volume and textural properties. STEM images showed well-dispersed Cu NPs on SILPs with a mean diameter varying from 3.6 to 4.6 nm depending on the triazolium cation used. Besides, XPS results suggest that the Cu(0)/Cu(I) ratio can be modulated by the electronic density of triazolium substituents. XPS and computational analysis gave mechanistic insights into the Cu NP stabilisation pathways, where the presence of electron-rich groups attached to a triazolium ring plays a critical role in leading to a cation adsorption pathway (Eads = 72 kcal mol−1). In contrast, less electron-rich groups favour the anion adsorption pathway (Eads = 63 kcal mol−1). The Cu@SILP composite with electron-rich groups showed the highest activity for the C–N Ullmann coupling reaction, which suggests that electron-rich groups might act as an electron-like reservoir to facilitate oxidative addition for N-arylation. This strategy firmly suggests the strong dependence of the nature of triazolium-based SILPs on the Cu NP surface active sites, which may provide a new environment to confine and stabilise MNPs for catalytic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...