Reactivity towards nitriles, cyanamides, and carbodiimides of palladium complexes derived from benzyl alcohol. Synthesis of a mixed Pd2Ag complex†
Abstract
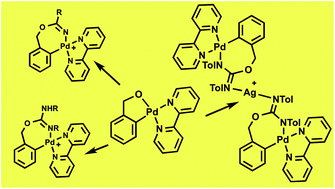
The chelate complex [Pd(κ2-C,O-C6H4CH2O-2)(bpy)] (II) reacts with acetonitrile, cyanamides, or carbodiimides, in the presence of AgOTf (1 : 5 : 1 molar ratio) and residual water, to form complexes [Pd{κ2-C,N-C6H4{CH2OC(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NX)Y}-2}(bpy)](OTf), where X = H, Y = Me (1), NMe2 (2a), NEt2 (2b), X = R, Y = NHR (R = iPr (3a), Tol (3b)), as a result of the insertion of the unsaturated reagent into the O–Pd bond of II and the protonation of one of the N atoms. In the absence of AgOTf the reaction of II with TolN
NX)Y}-2}(bpy)](OTf), where X = H, Y = Me (1), NMe2 (2a), NEt2 (2b), X = R, Y = NHR (R = iPr (3a), Tol (3b)), as a result of the insertion of the unsaturated reagent into the O–Pd bond of II and the protonation of one of the N atoms. In the absence of AgOTf the reaction of II with TolN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NTol (Tol = p-Tolyl) results in the formation of the neutral complex [Pd{κ2-C,N-C6H4{CH2OC(
NTol (Tol = p-Tolyl) results in the formation of the neutral complex [Pd{κ2-C,N-C6H4{CH2OC(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NTol)NTol}-2}(bpy)] (4). Complexes 3b and 4 can be interconverted by deprotonation (3b + KOtBu) or protonation (4 + KOTf + HOTf) reactions. When the reaction of II with TolN
NTol)NTol}-2}(bpy)] (4). Complexes 3b and 4 can be interconverted by deprotonation (3b + KOtBu) or protonation (4 + KOTf + HOTf) reactions. When the reaction of II with TolN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NTol in the presence of AgOTf is carried out in a 1 : 1 : 1 stoichiometric ratio, or for a short period of time, a mixture of 3b and a mixed heterometallic Ag2Pd complex 5 is obtained (5 = [Ag(N-4)2](OTf)). Complex 5 is the major product when the AgOTf is added before the carbodiimide, and the reaction is stopped immediately. 5 can also be obtained by reaction of 4 with 0.5 equiv. of AgOTf. When complex [PdI(C6H4CH2OH-2)(bpy)] (I) reacts with iPrN
NTol in the presence of AgOTf is carried out in a 1 : 1 : 1 stoichiometric ratio, or for a short period of time, a mixture of 3b and a mixed heterometallic Ag2Pd complex 5 is obtained (5 = [Ag(N-4)2](OTf)). Complex 5 is the major product when the AgOTf is added before the carbodiimide, and the reaction is stopped immediately. 5 can also be obtained by reaction of 4 with 0.5 equiv. of AgOTf. When complex [PdI(C6H4CH2OH-2)(bpy)] (I) reacts with iPrN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NiPr in the presence of TlOTf, instead of AgOTf, a ca. 1 : 1 mixture of 3a and [Pd{κ2-O,N-OCH2{C6H4{C(
NiPr in the presence of TlOTf, instead of AgOTf, a ca. 1 : 1 mixture of 3a and [Pd{κ2-O,N-OCH2{C6H4{C(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NHiPr)NiPr}-2}}(bpy)](OTf) (6) forms. Complex 6 is the result of the insertion of the carbodiimide into the C–Pd bond. Complexes 1–6 have been extensively characterized by NMR spectroscopy, and the crystal structures of 2a, 3a, and 5·2.5CHCl3·0.5Et2O have been determined by X-ray diffraction studies.
NHiPr)NiPr}-2}}(bpy)](OTf) (6) forms. Complex 6 is the result of the insertion of the carbodiimide into the C–Pd bond. Complexes 1–6 have been extensively characterized by NMR spectroscopy, and the crystal structures of 2a, 3a, and 5·2.5CHCl3·0.5Et2O have been determined by X-ray diffraction studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...