Ag-triggered Co4+ active sites enable OH* nucleophilic attack for efficient electrocatalytic oxidation of alcohols to acids
Abstract
The selective oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids is a widely employed transformation in organic chemistry. However, the intrinsic mechanism by which R(Ph)–OH (R is an alkyl or phenyl) in alcohols undergoes dehydrogenation to form oxygen-rich acids remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate an efficient cooperative interface structure (Ag/Co(OH)2) as an electrocatalyst. Ag/Co(OH)2 significantly lowers the energy barrier of the rate-determining step 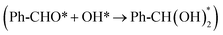 to 0.78 eV and enhances the chemisorption energy of the Ph-CHO* intermediate to −0.89 eV, both superior to Co(OH)2 (ΔG = 1.22 eV, Gads = −0.72 eV), and the faradaic efficiency for carboxylic acids reached 99.6% under mild conditions. Kinetic studies reveal the formation of Co4+–O species on the composite surface, promoting the capture of OH*. Furthermore, Ag/Co(OH)2 also demonstrates excellent faradaic efficiencies (ranging from 41.48% to 88.73%) in the oxidation of methanol, furfuryl alcohol, ethylene glycol, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to their corresponding carboxylic acids. This work provides a new idea for designing efficient and stable catalysts for electrocatalytic carboxylic acid synthesis.
to 0.78 eV and enhances the chemisorption energy of the Ph-CHO* intermediate to −0.89 eV, both superior to Co(OH)2 (ΔG = 1.22 eV, Gads = −0.72 eV), and the faradaic efficiency for carboxylic acids reached 99.6% under mild conditions. Kinetic studies reveal the formation of Co4+–O species on the composite surface, promoting the capture of OH*. Furthermore, Ag/Co(OH)2 also demonstrates excellent faradaic efficiencies (ranging from 41.48% to 88.73%) in the oxidation of methanol, furfuryl alcohol, ethylene glycol, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to their corresponding carboxylic acids. This work provides a new idea for designing efficient and stable catalysts for electrocatalytic carboxylic acid synthesis.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...