Impacts of vacancy defects and element substitution on the electrical transport properties of θ-Al2Cu and
 : A NEGF-DFT study
: A NEGF-DFT study
Abstract
Defects have been shown to play a significant role in the regulation of the mechanical properties of Al2Cu, and their impact on transport properties cannot be disregarded. In this paper, the effects of vacancy defects and substitutional defects on the transport properties of θ-Al2Cu and 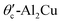 were systematically investigated based on the non-equilibrium Green's function combined with density functional theory. The results demonstrate that the transport properties of θ-Al2Cu are superior to those of
were systematically investigated based on the non-equilibrium Green's function combined with density functional theory. The results demonstrate that the transport properties of θ-Al2Cu are superior to those of 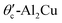 . For the θ-Al2Cu system, the formation energy of Al vacancies is lower than that of Cu vacancies, indicating that Al vacancies are more likely to form. Nevertheless, Al vacancies cause a greater reduction in conductance than Cu vacancies. Therefore, the generation of Al vacancies should be minimized for practical applications. The influence of substitutional defects on transport properties is contingent on the matching degree in the atomic radii and chemical bonding properties between dopant atoms and host atoms. Impurity atoms with large differences in size or chemical bonding properties have been shown to enhance local potential barriers and electron scattering, thereby reducing transport performance. Besides, low-symmetry structures exhibit heightened sensitivity to such disturbances. Consequently, θ-Al2Cu could be a promising candidate for interconnect applications, provided Al vacancies are controlled and substitutional dopants are selected for minimal size and bonding disruption.
. For the θ-Al2Cu system, the formation energy of Al vacancies is lower than that of Cu vacancies, indicating that Al vacancies are more likely to form. Nevertheless, Al vacancies cause a greater reduction in conductance than Cu vacancies. Therefore, the generation of Al vacancies should be minimized for practical applications. The influence of substitutional defects on transport properties is contingent on the matching degree in the atomic radii and chemical bonding properties between dopant atoms and host atoms. Impurity atoms with large differences in size or chemical bonding properties have been shown to enhance local potential barriers and electron scattering, thereby reducing transport performance. Besides, low-symmetry structures exhibit heightened sensitivity to such disturbances. Consequently, θ-Al2Cu could be a promising candidate for interconnect applications, provided Al vacancies are controlled and substitutional dopants are selected for minimal size and bonding disruption.




 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
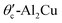 : A NEGF-DFT study
: A NEGF-DFT study