Poly(ether-imide-ester)s incorporating sulfur-containing amino acids: a first step toward more sustainable high-dielectric polymer materials
Abstract
The development of high-dielectric polymer materials is critical for advancing energy storage and conversion technologies. In this study, we report the synthesis and characterization of novel poly(ether-imide-ester) (PEIE) polymers incorporating sulfur-based amino acid residues as dipolar units. Specifically, we designed and synthesized two PEIEs containing methionine (PEIE-Met) and its oxidized form, methionine sulfone (PEIE-Met(O2)), to investigate the impact of pendant thioether and sulfone groups on the dielectric properties. The synthesized polymers were thoroughly characterized via spectroscopic (FTIR, NMR), thermal (TGA, DSC), and dielectric (BDS) techniques. The results confirm the successful incorporation of methionine-based moieties into the polymer backbone, leading to the formation of materials showing high thermal stability, as evidenced by onset degradation temperatures above 300 °C, glass transition temperatures (Tg) in the 162–182 °C range, and excellent dielectric performance. Notably, at room temperature, PEIE-Met(O2) exhibited a higher dielectric constant 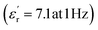 than PEIE-Met did
than PEIE-Met did 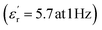 , which was attributed to the increased dipole moment of the sulfone groups. Both polymers maintained low dielectric loss values (tan(δ) < 0.01) at room temperature, making them promising candidates for capacitor applications. Notably, the materials developed in this work exhibited discharge efficiency values above 85% at 100 °C under electric fields of 100 and 200 MV m−1, confirming their suitability as dielectric layers for energy storage applications. This study highlights the potential of bioderived amino acid residues as functional building blocks for high-dielectric polymer design. Our findings open new avenues for the development of sustainable, high-performance dielectric materials tailored for next-generation electronic and energy storage applications.
, which was attributed to the increased dipole moment of the sulfone groups. Both polymers maintained low dielectric loss values (tan(δ) < 0.01) at room temperature, making them promising candidates for capacitor applications. Notably, the materials developed in this work exhibited discharge efficiency values above 85% at 100 °C under electric fields of 100 and 200 MV m−1, confirming their suitability as dielectric layers for energy storage applications. This study highlights the potential of bioderived amino acid residues as functional building blocks for high-dielectric polymer design. Our findings open new avenues for the development of sustainable, high-performance dielectric materials tailored for next-generation electronic and energy storage applications.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...