Influence of polymer network structure on the elastic and fracture properties of polyacrylamide hydrogel†
Abstract
The elastic and fracture properties of hydrogels are strongly influenced by the polymer network structure. The hydrogel network is similar to the extracellular matrix (ECM) of tissues. The network structure of the hydrogel can be varied by varying the polymer volume fraction (ϕ) and crosslinker concentration (C). In this work, the polymer network structure is varied at the preparation state. The elastic modulus (E) values were obtained by hydrogel beam bending experiments. We investigated the influence of network structure on the fracture characteristics of polyacrylamide hydrogel during the deep insertion of a hypodermic needle. The needle insertion experiments were performed using a hypodermic needle at a constant insertion speed. We find that the elastic modulus, measured by beam bending experiments, linearly increases with ϕ2C. The needle insertion induced cone crack fracture, showing that the fracture energy is proportional to 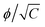 . Furthermore, the periodicity of the cone cracks and cone angles are strongly influenced by the crosslinker concentration and polymer volume fraction. The periodicity of the cone crack linearly increased with
. Furthermore, the periodicity of the cone cracks and cone angles are strongly influenced by the crosslinker concentration and polymer volume fraction. The periodicity of the cone crack linearly increased with 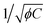 . These results provide a better understanding of the fracture processes of soft tissues with various water concentrations and different ECM structures, such as the lungs, liver, and brain, during needle biopsies.
. These results provide a better understanding of the fracture processes of soft tissues with various water concentrations and different ECM structures, such as the lungs, liver, and brain, during needle biopsies.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...