CO2-sensitive inks for the rapid measurement of total viable count (TVC) using micro-respirometry†
Abstract
At present, micro-respirometry for measuring total viable count, O2 μR-TVC, is based on the time taken, TT, for an inoculum to significantly reduce the dissolved O2 level (typically from 21% to ≤ 10.5%). Here, a simple kinetic model relevant to μR-TVC is presented which describes the growth of the bacteria from an initial inoculum, No, to a maximum level, Nmax, and concomitant consumption of O2 and generation of CO2, in which the half-way time point, 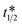 , corresponds to Nmax/No = 0.5, at which point %O2 = %CO2 = 10.5%. The model shows that it is not possible to reduce the TT in O2 μR-TVC below
, corresponds to Nmax/No = 0.5, at which point %O2 = %CO2 = 10.5%. The model shows that it is not possible to reduce the TT in O2 μR-TVC below 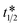 , as TT increases above
, as TT increases above 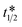 with increasing sensitivity of the O2 sensor. In contrast, the same model shows that if a CO2 sensor is used instead, TT can be reduced significantly below
with increasing sensitivity of the O2 sensor. In contrast, the same model shows that if a CO2 sensor is used instead, TT can be reduced significantly below 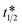 and consequently CO2 μR-TVC could be made much faster than conventional O2 μR-TVC. To test this model prediction, a range of colourimetric CO2 sensors of varying sensitivity, α, were prepared and used to make CO2 μR-TVC measurements. The results confirm that the greater the sensitivity of the sensor, the shorter the TT, as predicted by the kinetic model. Two CO2 indicators, one of moderate sensitivity and one of high sensitivity were used to generate straight-line log(CFU mL−1) vs. TT calibration plots, which can then be used to determine the unknown TVCs of subsequent samples. The future of CO2 μR-TVC as a possible new, faster alternative to conventional O2 μR-TVC is discussed briefly.
and consequently CO2 μR-TVC could be made much faster than conventional O2 μR-TVC. To test this model prediction, a range of colourimetric CO2 sensors of varying sensitivity, α, were prepared and used to make CO2 μR-TVC measurements. The results confirm that the greater the sensitivity of the sensor, the shorter the TT, as predicted by the kinetic model. Two CO2 indicators, one of moderate sensitivity and one of high sensitivity were used to generate straight-line log(CFU mL−1) vs. TT calibration plots, which can then be used to determine the unknown TVCs of subsequent samples. The future of CO2 μR-TVC as a possible new, faster alternative to conventional O2 μR-TVC is discussed briefly.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...