Solubility, speciation and thermodynamics of Fe in reducing aqueous KCl solutions
Abstract
The solubility of two well-characterized Fe(II) solid phases (i.e., Fe(OH)2(cr) and Fe2(OH)3Cl(cr)) were investigated in batch undersaturation solubility experiments conducted over a wide range of pHm (7.5 ≤ pHm ≤ 10.5) and ionic strength (0.01 M ≤ I ≤ 4.0 M KCl). Solid phase characterization was carried out using XRD including Rietveld analysis, providing key insights into their phase composition and crystallite size. Chemical, thermodynamic and SIT activity models were derived for the system Fe2+–K+–H+–Cl−–OH−–H2O(l) on the basis of the comprehensive experimental dataset. Solubility constants determined in this work 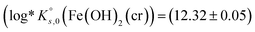 and
and 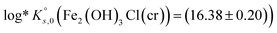 contribute to improving the description of Fe chemistry under very reducing conditions, and can be implemented in thermodynamic databases and geochemical calculations of relevance, e.g. in the context of nuclear waste disposal.
contribute to improving the description of Fe chemistry under very reducing conditions, and can be implemented in thermodynamic databases and geochemical calculations of relevance, e.g. in the context of nuclear waste disposal.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...