Comprehensive structural insights and electrochemical evaluation of rhamnose and salicin for green corrosion protection of carbon steel in acidic medium
Abstract
This study presents a comprehensive electrochemical and theoretical evaluation of two naturally occurring organic compounds, Rhamnose and Salicin, as green corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in 1 M HCl. Electrochemical techniques including Potentiodynamic Polarization (PDP), Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), and Electrochemical Frequency Modulation (EFM) were employed to assess inhibition performance. At a concentration of 1.0 × 10−3 M, Salicin achieved a maximum inhibition efficiency of 96.10%, while Rhamnose reached 91.91%, as determined by PDP. EIS analysis revealed a significant increase in charge transfer resistance (Rct) from 19.05 Ω cm2 (blank) to 172.27 Ω cm2 for Salicin and 121.65 Ω cm2 for Rhamnose. The adsorption behavior followed the Langmuir isotherm, with calculated free energies of adsorption 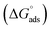 of −33.21 kJ mol−1 for Salicin and −32.59 kJ mol−1 for Rhamnose, indicating spontaneous mixed-mode adsorption. Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations revealed that Salicin possesses a lower energy gap (ΔE = 6.321 eV) and higher electron transfer capability (ΔN = 0.943) compared to Rhamnose (ΔE = 8.767 eV, ΔN = 0.783), suggesting superior reactivity and adsorption potential. Adsorption locator simulations confirmed stronger binding of Salicin to Fe(110) surfaces, with an adsorption energy of −230.86 kcal mol−1 versus −83.58 kcal mol−1 for Rhamnose. These findings highlight the potential of Salicin as a highly efficient, eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor and demonstrate the value of integrating molecular-level insights into inhibitor design.
of −33.21 kJ mol−1 for Salicin and −32.59 kJ mol−1 for Rhamnose, indicating spontaneous mixed-mode adsorption. Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations revealed that Salicin possesses a lower energy gap (ΔE = 6.321 eV) and higher electron transfer capability (ΔN = 0.943) compared to Rhamnose (ΔE = 8.767 eV, ΔN = 0.783), suggesting superior reactivity and adsorption potential. Adsorption locator simulations confirmed stronger binding of Salicin to Fe(110) surfaces, with an adsorption energy of −230.86 kcal mol−1 versus −83.58 kcal mol−1 for Rhamnose. These findings highlight the potential of Salicin as a highly efficient, eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor and demonstrate the value of integrating molecular-level insights into inhibitor design.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...