Ligand-to-ligand charge transfer in anthracene-based cyclic trinuclear complexes for enhancing photocatalytic deprotection of Weinreb amides†
Abstract
The development of efficient, visible-light-responsive photocatalysts remains critical for advancing sustainable chemical synthesis. Herein, we report a photosensitive cyclic trinuclear complex (CTC), An-Au3, featuring an anthracene (donor) and trifluoromethyl (acceptor)-modified pyrazole ligand (donor–π–acceptor type ligand engineering), where the anthracene chromophore and weak metallophilic interactions work synergistically to enhance visible-light absorption and solubility. The complex exhibits moderate excited state and ground state potentials (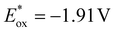 , Ered = −2.10 V vs. SCE), displaying enhanced catalytic efficiency (up to 99% yield) in the photocatalytic deprotection of Weinreb amides. Ultrafast spectroscopy and theoretical analyses confirm an intramolecular ligand-to-ligand charge transfer (LLCT) mechanism, while mechanistic studies unveil substrate-dependent oxidative/reductive quenching cycles. This work not only enriches the variety of CTC complexes but also provides design concepts that enhance the functionality of metal-complex photocatalysts for future applications.
, Ered = −2.10 V vs. SCE), displaying enhanced catalytic efficiency (up to 99% yield) in the photocatalytic deprotection of Weinreb amides. Ultrafast spectroscopy and theoretical analyses confirm an intramolecular ligand-to-ligand charge transfer (LLCT) mechanism, while mechanistic studies unveil substrate-dependent oxidative/reductive quenching cycles. This work not only enriches the variety of CTC complexes but also provides design concepts that enhance the functionality of metal-complex photocatalysts for future applications.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...