Exploring hot melt extrusion in the formation of exemestane/amino acid co-amorphous systems
Abstract
Co-amorphous systems (CAMS) of exemestane (EXE) were prepared with three amino acid (AA) co-formers of increasing hydrophobicity: (i) L-lysine (LYS), (ii) L-valine (VAL) and (iii) L-methionine (MET) using feed solvent pretreatment hot-melt extrusion (mHME). Thermal analysis (DSC and TGA) guided processing parameters confirmed the class III glass-forming ability of EXE (Tg = 91.2 °C). Hansen solubility parameters (Δδt < 4 MPa1/2) predicted favorable drug/co-former miscibility. PXRD and DSC demonstrated successful co-amorphization for molar ratios of EXE/LYS (1 : 1 and 1 : 2), EXE/MET (1 : 1) and EXE/VAL (2 : 1 drug/AA). ATR-FTIR indicated co-amorphization predominantly by simple molecular mixing with only weak interactions. The physical stability of CAMS was evaluated by isothermal microcalorimetry, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and crystallographic profiles (pXRD) obtained at different times during accelerated stability tests (40 °C, 75% RH). EXE/LYS systems exhibited the longest relaxation times (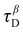 ), translating as excellent physical stability, which corroborated the results of accelerated tests. EXE/MET showed moderate stabilization, while EXE/VAL was the least stable. Under non-sink conditions of the dissolution test, EXE/LYS (1 : 1) presented a pronounced spring–parachute profile with sustained supersaturation, outperforming other EXE/AA CAMS.
), translating as excellent physical stability, which corroborated the results of accelerated tests. EXE/MET showed moderate stabilization, while EXE/VAL was the least stable. Under non-sink conditions of the dissolution test, EXE/LYS (1 : 1) presented a pronounced spring–parachute profile with sustained supersaturation, outperforming other EXE/AA CAMS.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...