In vitro and in vivo validation studies of optimized iron oxide nanoparticles carrying targeting ligands for a new therapeutic strategy in head and neck cancers
Abstract
Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) are increasingly used in the biomedical field. Indeed, they can improve patient diagnosis, as they are excellent T2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and they can be considered a therapeutic and radiosensitizing agent for cancer by influencing the redox balance. However, to achieve specific accumulation of nanoparticles in the tumor, active targeting with specific ligands is required. In this context, we have developed IONPs that would specifically target head and neck cancer (HNC) cells. First, we optimized IONP synthesis and produced dendronized IONPs that were coupled with the targeting ligand cRGD (@D + cRGD IONPs) or peptide 22 (@D + P22 IONPs). The former is a tripeptide with affinity for integrins while the latter is a dodecapeptide analog of GE11, an EGF (epidermal growth factor) derived polypeptide with affinity for EGFR. EGFR is overexpressed in these HNC cells. Next, we highlighted the interest of using @D + P22 IONPs in order to enhance internalization of IONPs in vitro. Furthermore, we evaluated the biodistribution of IONPs in vivo and showed by MRI an immediate T2 contrast in the liver and kidney, whatever the type of IONP. Finally, we developed an in vivo model of mice with FaDu xenografts and showed by 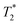 MRI a tendency for higher accumulation of @D + P22 IONPs (10.1% decrease of T2 calculated in the tumoral region by
MRI a tendency for higher accumulation of @D + P22 IONPs (10.1% decrease of T2 calculated in the tumoral region by 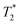 measurement) compared to @D IONPs (0.15%) within the tumors. These preliminary results are encouraging and require further investigations, but they suggest the potential interest of using this IONP model for targeting EGFR-positive tumors.
measurement) compared to @D IONPs (0.15%) within the tumors. These preliminary results are encouraging and require further investigations, but they suggest the potential interest of using this IONP model for targeting EGFR-positive tumors.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...