af2rave: protein ensemble generation with physics-based sampling†
Abstract
We introduce 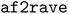 , an open-source Python package that implements an improved and automated version of our previous AlphaFold2-RAVE protocol. AlphaFold2-RAVE integrates machine learning-based structure prediction with physics-driven sampling to generate alternative protein conformations efficiently. It has been well established that protein structures are not static but exist as ensembles of conformations, many of which are functionally relevant yet challenging to resolve experimentally. While deep learning models like AlphaFold2 can predict structural ensembles, they lack explicit physical validation. The Alphafold2-RAVE family of methods addresses this limitation by combining reduced multiple sequence alignment (MSA) AlphaFold2 predictions with biased or unbiased molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to efficiently explore local conformational space. Compared to our previous work, the current workflow significantly reduced the required amount of a priori knowledge about a system to allow the user to focus on the conformation diversity they would like to sample. This is achieved by a feature selection module to automatically pickup the important collective variables to monitor. The improved workflow was validated on multiple systems with the package
, an open-source Python package that implements an improved and automated version of our previous AlphaFold2-RAVE protocol. AlphaFold2-RAVE integrates machine learning-based structure prediction with physics-driven sampling to generate alternative protein conformations efficiently. It has been well established that protein structures are not static but exist as ensembles of conformations, many of which are functionally relevant yet challenging to resolve experimentally. While deep learning models like AlphaFold2 can predict structural ensembles, they lack explicit physical validation. The Alphafold2-RAVE family of methods addresses this limitation by combining reduced multiple sequence alignment (MSA) AlphaFold2 predictions with biased or unbiased molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to efficiently explore local conformational space. Compared to our previous work, the current workflow significantly reduced the required amount of a priori knowledge about a system to allow the user to focus on the conformation diversity they would like to sample. This is achieved by a feature selection module to automatically pickup the important collective variables to monitor. The improved workflow was validated on multiple systems with the package 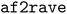 , including E. coli adenosine kinase (ADK) and human DDR1 kinase, successfully identifying distinct functional states with minimal prior biological knowledge. Furthermore, we demonstrate that
, including E. coli adenosine kinase (ADK) and human DDR1 kinase, successfully identifying distinct functional states with minimal prior biological knowledge. Furthermore, we demonstrate that 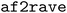 achieves conformational sampling efficiency comparable to long unbiased MD simulations on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain while significantly reducing the computational cost. The
achieves conformational sampling efficiency comparable to long unbiased MD simulations on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain while significantly reducing the computational cost. The 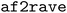 package provides a streamlined workflow for researchers to generate and analyze alternative protein conformations, offering an accessible tool for drug discovery and structural biology.
package provides a streamlined workflow for researchers to generate and analyze alternative protein conformations, offering an accessible tool for drug discovery and structural biology.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...