Developing large language models for quantum chemistry simulation input generation†
Abstract
Scientists across domains are often challenged to master domain-specific languages (DSLs) for their research, which are merely a means to an end but are pervasive in fields like computational chemistry. Automated code generation promises to overcome this barrier, allowing researchers to focus on their core expertise. While large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in synthesizing code from natural language prompts, they often struggle with DSLs, likely due to their limited exposure during training. In this work, we investigate the potential of foundational LLMs for generating input files for the quantum chemistry package ORCA by establishing a general framework that can be adapted to other DSLs. To improve upon 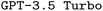 as our base model, we explore the impact of prompt engineering, retrieval-augmented generation, and finetuning via synthetically generated datasets. We find that finetuning, even with synthetic datasets as small as 500 samples, significantly improves performance. Additionally, we observe that finetuning shows synergism with advanced prompt engineering such as chain-of-thought prompting. Consequently, our best finetuned models outperform the formally much more powerful
as our base model, we explore the impact of prompt engineering, retrieval-augmented generation, and finetuning via synthetically generated datasets. We find that finetuning, even with synthetic datasets as small as 500 samples, significantly improves performance. Additionally, we observe that finetuning shows synergism with advanced prompt engineering such as chain-of-thought prompting. Consequently, our best finetuned models outperform the formally much more powerful 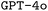 model. In turn, finetuning GPT-4o with the same small synthetic dataset leads to a further substantial performance improvement, suggesting our approach to be more general rather than limited to LLMs with poor base proficiency. All tools and datasets are made openly available for future research. We believe that this research lays the groundwork for a wider adoption of LLMs for DSLs in chemistry and beyond.
model. In turn, finetuning GPT-4o with the same small synthetic dataset leads to a further substantial performance improvement, suggesting our approach to be more general rather than limited to LLMs with poor base proficiency. All tools and datasets are made openly available for future research. We believe that this research lays the groundwork for a wider adoption of LLMs for DSLs in chemistry and beyond.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...