Observation of competing magnetic phases, mechanical stability, electronic structure, magnetism, and remarkable thermoelectric aspects of Ba2GdRuO6
Abstract
The Ba2GdRuO6 double perovskite oxide demonstrates intriguing behavior, arising from competing antiferromagnetic (AFM) and ferrimagnetic (FiM) phases. Under the GGA+U+SOC scheme, the system exhibits an AFM ground state with a very small energy difference of −11.39 meV compared to the FiM one. In contrast, spin modeling reveals significant magnetic frustrations along the z-axis and favors the FiM phase. Also, the magnetic phase transition discloses a Curie temperature (TC) of 60 K. Additionally, magnetization measurements also affirm the FiM nature which loses saturation at higher temperatures, indicating a transition from FiM to paramagnetic, above TC. The electronic structure displays the semiconductor nature owing to a direct energy gap of 1.04/0.89 eV in the AFM/FiM state. The determined spin moments on the Gd(1–2)/Ru(1–2) and Gd(3–4)/Ru(3–4) ions are +6.9/+2.0μB and −6.9/−2.0μB in the AFM spin–orbit, respectively, while they are +6.89/−2.0 on the Gd(1–4)/Ru(1–4) ion in the FiM one. It is found that the Gd3+ and Ru4+ ions lie in +3(4f7) and +4(4d4) valence states with electronic configurations [fx(x2−3y2)]↑0↓1 [fy(3x2−y2)]↑0↓1 [fz(x2−y2)]↑0↓1 [fxyz]↑0↓1 [fxz2]↑0↓1 [fyz2]↑0↓1 [fz3]↑0↓1 and t32g↑t12g↓e0g↑e0g↓ with spin quantum numbers of 7/2 and 1, correspondingly. Furthermore, the mechanical stability of the material is validated by satisfying the Born stability criteria and the ductility is determined using Pugh's ratio 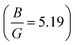 . Noticeably, the presence of a positive Cauchy pressure of 66.53 GPa further supports the ionic nature of the motif. Besides, the system illustrates a positive Seebeck coefficient, indicating holes as the dominant charge carriers with the highest value of 279 μV K−1 at 400 K. Remarkably, the system achieves a high figure of merit of 0.86 at 550 K even with the inclusion of lattice thermal conductivity, as well as sustaining excellent thermoelectric performance, suggesting a strong potential for elevated temperature energy harvesting applications along with spintronics.
. Noticeably, the presence of a positive Cauchy pressure of 66.53 GPa further supports the ionic nature of the motif. Besides, the system illustrates a positive Seebeck coefficient, indicating holes as the dominant charge carriers with the highest value of 279 μV K−1 at 400 K. Remarkably, the system achieves a high figure of merit of 0.86 at 550 K even with the inclusion of lattice thermal conductivity, as well as sustaining excellent thermoelectric performance, suggesting a strong potential for elevated temperature energy harvesting applications along with spintronics.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...