Biocompatible metal–organic frameworks as promising platforms to eradicate HIV reservoirs ex vivo in people living with HIV†
Abstract
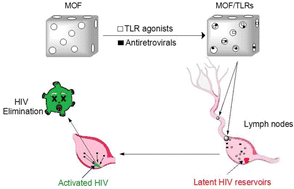
The HIV attacks the immune system provoking an infection that is considered a global health challenge. Despite antiretroviral treatments being effective in reducing the plasma viral load in the blood to undetectable levels in people living with HIV (PLWH), the disease is not cured and has become chronic. This happens because of the existence of anatomical and cellular viral reservoirs, mainly located in the lymph nodes and gastrointestinal tract, which are composed of infected CD4+ T cells with a resting memory phenotype and inaccessible to antiretroviral therapy. Herein, a new therapeutic strategy based on nanotechnology is presented. Different combinations of antiretroviral drugs (bictegravir/tenofovir/emtricitabine and nevirapine/tenofovir/emtricitabine) and toll-like receptor agonists were encapsulated into metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) PCN-224 and ZIF-8. The encapsulation efficiencies of all the drugs, as well as their release rate from the carriers, were measured. In vitro studies about the cell viability, the hemocompatibility, and the platelet aggregation of the MOFs were carried out. Epifluorescence microscopy assays confirmed the ability of ZIF-8 to target a carboxyfluorescein probe inside HeLa cell lines and PBMCs. These results pave the way for the use of these structures to eliminate latent HIV reservoirs from anatomical compartments through the activation of innate immune cells, and a higher efficacy of the triplet combinations of antiretroviral drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...