Microwave-enhanced antibacterial activity of polydopamine–silver hybrid nanoparticles†
Abstract
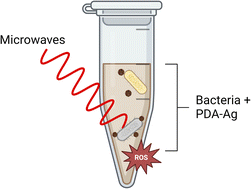
The ever-increasing risks posed by antibiotic-resistant bacteria have stimulated considerable interest in the development of novel antimicrobial strategies, including the use of nanomaterials that can be activated on demand and result in irreversible damage to pathogens. Microwave electric field-assisted bactericidal effects on representative Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial strains were achieved in the presence of hybrid polydopamine–silver nanoparticles (PDA–Ag NPs) under low-power microwave irradiation using a resonant cavity (1.3 W, 2.45 GHz). A 3-log reduction in the viability of bacterial populations was observed within 30 minutes which was attributed to the attachment of PDA–Ag NPs and associated membrane disruption in conjunction with the production of intra-bacterial reactive oxygen species (ROS). A synergistic effect between PDA and Ag has been demonstrated whereby PDA acts both as an Ag NP carrier and a microwave enhancer. These properties together with the remarkable adhesivity of PDA are opening a route to design of antibacterial adhesives and surface coatings for prevention of biofilm formation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: RSC Advances Nanoscience year in review 2024


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...