Indocyanine green within glycosylated polymeric micelles as potential image agents to map sentinel lymph nodes and breast cancer†
Abstract
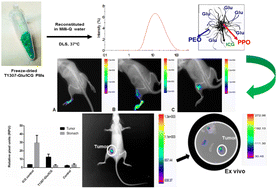
Indocyanine green (ICG) is an FDA-approved near-infrared (NIR) dye used as a contrast agent for medical diagnosis in such techniques as image-guided surgery (IGS) and IGS-supported mapping for sentinel lymph node biopsy (SNLB). However, there are numerous disadvantages to its use in clinical applications: (i) self-aggregation in solution, (ii) poor targeting and (iii) short half-life in vivo, due to the rapid uptake by the liver. Herein, to overcome these obstacles, we utilized polymeric micelles (PMs) based on the amphiphilic linear and branched block poly(ethylene oxide)–poly(propylene oxide) (PEO–PPO) copolymers (Pluronic® and Tetronic®) for ICG stabilization, vehicleization and to directionally target breast cancer tissues. Because of their singular properties, PMs offer several advantages such as the ability to modify their surfaces with a variety of receptor-targeting ligands and their nano-scale size, which is suitable for taking advantage of the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect for cancer diagnosis. In this work, we prepared ICG within pristine F127 and T1307 and their glucosylated derivatives (F127-Glu and T1307-Glu, respectively). These systems have a sub-30 nm-nanosized hydrodynamic diameter (19–27 nm), moderate negative Z-potentials (until −10 mV), and satisfactory stability in water even after lyophilisation and reconstitution, at 25 and 37 °C, respectively. Particularly, ICG within T1307-Glu PMs displayed maximum solubility and excellent encapsulation efficiency (100%), with a potentially large in vivo uptake according to high specificity and efficacious capture in lymph nodes (LNs) and tumors. All the results presented in this work, indicate that ICG-loaded PMs can potentially be used as image probe agents for IGS, SLNB and breast cancer imaging.
- This article is part of the themed collection: World Cancer Day 2025: Showcasing cancer research across the RSC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...