On the mechanism of carboxylate elimination from carbohydrate monoester-derived radicals†
Abstract
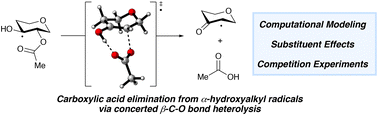
A computational study of the mechanism of hydrogen atom transfer-induced carboxylate elimination from monoacylated 1,2-diol groups in pyranosides is presented. A comprehensive analysis of the 1,2-migration, elimination and fragmentation pathways reveals that concerted elimination via a 7-membered, hydrogen-bonded transition state is favored. Relative rates of elimination inferred from an intramolecular competition experiment are consistent with the trends obtained from the calculations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Computational Organic Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...