SARS-CoV-2-induced disruption of a vascular bed in a microphysiological system caused by type-I interferon from bronchial organoids†
Abstract
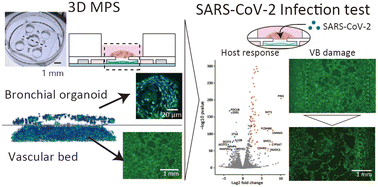
Blood vessels show various COVID-19-related conditions including thrombosis and cytokine propagation. Existing in vitro blood vessel models cannot represent the consequent changes in the vascular structure or determine the initial infection site, making it difficult to evaluate how epithelial and endothelial tissues are damaged. Here, we developed a microphysiological system (MPS) that co-culture the bronchial organoids and the vascular bed to analyze infection site and interactions. In this system, virus-infected organoids caused damage in vascular structure. However, vasculature was not damaged or infected when the virus was directly introduced to vascular bed. The knockout of interferon-related genes and inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway reduced the vascular damage, indicating the protective effect of interferon response suppression. The results demonstrate selective infection of bronchial epithelial cells and vascular damage by cytokines and also indicate the applicability of MPS to investigate how the infection influences vascular structure and functions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...