Strategies to enable microsized alloy anodes for high-energy and long-life alkali-ion batteries†
Abstract
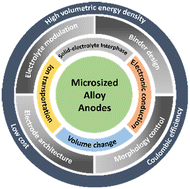
Micro-sized anode materials demonstrate greater potential for practical applications than nanomaterials in the aspects of volumetric energy density, coulombic efficiency, fabrication process, and cost. However, the huge volume changes of alloy anodes (up to ∼500%) during repeated charge/discharge has led to a series of challenging issues including pulverization of active material particles and delamination from current collectors, formation of thick and fragile solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) and depletion of electrolytes, eventually leading to rapid cell degradation. Herein, we review recent progress of rational strategies to enable the use of microsized alloy anodes (Si, P, Sb, Sn, etc.) including electrolyte modulation, binder design and architecture engineering. We also provide perspectives on future directions and remaining challenges of microsized anodes towards practical applications.
Keywords: Volume change; Alloy; Anodes; Microsized; Alkali-ion; Batteries.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Virtual Collection – Batteries and Energy Storage, Virtual Collections—ICM HOT Papers and Virtual Collections—ICM Reviews


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...