Chemoenzymatic β-specific methylene C(sp3)–H deuteration of carboxylic acids†
Abstract
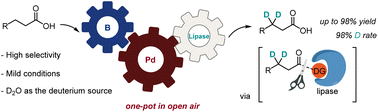
The combination of three types of catalysts in one pot, including borate, palladium, and lipase, enabled a one-pot β-specific methylene C(sp3)–H deuteration reaction of aliphatic acids using D2O. In the context of the widely used 8-aminoquinoline (8-AQ) directed C–H activation, this represented the first example of catalytic formation and cleavage of the directing group under mild conditions. Compared with previous deuteration methods, high chemo- and regioselectivity, high yields, and high deuterated rate were obtained without using environmentally unfriendly reagents such as strong acids, strong bases, or condensation reagents. The protocol was also amenable to the synthesis of α,α,β,β-tetradeuterated acids and various deuterated drug molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...