Regulating the type of nitrogen to improve the performance of Co–N/C with a confinement effect in peroxymonosulfate activation for the effective degradation of organic pollutants†
Abstract
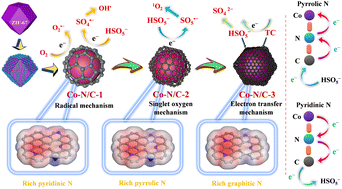
Water pollution has always been an issue of significant human concern, and the development of effective wastewater treatment processes is important. Herein, three Co–N/C-based catalysts with different types of nitrogen were fabricated and employed to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for tetracycline (TC) degradation. Due to the existence of a spatial confinement effect, all the Co–N/C-based catalysts showed excellent catalytic activities, and the removal efficiencies of TC were over 90% within 10 min. Notably, current results indicate that the Co–N/C-based catalyst rich in pyridinic N provides electrons to break the peroxy bonds of PMS for generating SO4˙−, while the Co–N/C-based catalyst containing more pyrrolic N acquires electrons from PMS to produce SO5˙−, which is further converted into 1O2. Moreover, the Co–N/C-based catalyst rich in graphitic N displayed good performance in electron transfer and can mediate the direct electron transfer process between TC and PMS. More interestingly, radical-induced oxidation exhibited a high TOC removal efficiency, but the corresponding anti-interference ability was weak. 1O2-induced oxidation and direct electron transfer process had a high removal efficiency for TC and good anti-interference ability, but the mineralization efficiency was relatively low. In short, the current work will provide a valuable reference for future research.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Environmental Science: Nano Recent HOT Articles and Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...