Discovery of mitochondrion-targeting copper(ii)-plumbagin and -bipyridine complexes as chemodynamic therapy agents with enhanced antitumor activity†
Abstract
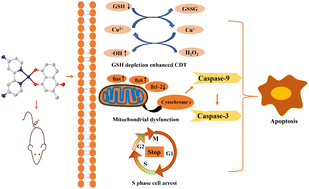
Four copper(II)-plumbagin and -bipyridine complexes (Cu1–Cu4) were synthesized as chemodynamic therapy agents with enhanced antitumor activity. As lipophilic and positively charged compounds, Cu1–Cu4 were preferentially accumulated in mitochondria and activated the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Mechanistic studies showed that Cu1–Cu4 reacted with GSH to reduce Cu2+ ions to Cu+ ions, catalyzed the formation of toxic hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) from hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) through a Fenton-like reaction, induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and activated caspase-9/3, which eventually led to apoptosis. Cu1–Cu4 arrested HeLa cells in the S phase and eventually killed cancer cells. Cu2 showed a favorable pharmacokinetic profile in mice. Moreover, Cu2 effectively inhibited the growth of HeLa xenografts in nude mice and showed low toxicity in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...