Determining the potential-dependent identity of methane adsorbates at Pt electrodes using EC-MS†
Abstract
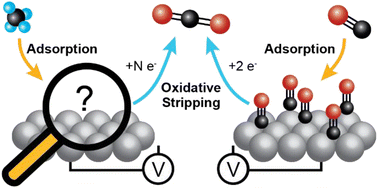
The increased availability of methane resulting from shale gas extraction and renewable feedstocks has made the development of technologies that can utilize this resource in a distributed setting a valuable target. Methane can be leveraged as a resource through its electrochemical partial oxidation to more valuable liquid chemicals, such as methanol, and its total oxidation to generate electricity. Enabling the partial and total oxidation of methane requires an understanding of the surface chemistry of methane under applied potentials. Herein we employ electrochemical mass spectrometry (EC-MS) to investigate the potential-dependent distribution of surface compounds generated from adsorbed methane under ambient conditions. By directly measuring the products of adsorbate oxidation using EC-MS we found that methane adsorption has a strong potential dependence with maximum adsorption at 0.3 V vs. RHE, and *CO is the dominant surface intermediate independent of the potential at which methane is adsorbed. Our findings explain why Pt is a poor catalyst for the electrocatalytic partial oxidation of methane and point the way to better catalyst materials for electrocatalytically valorizing methane in chemical synthesis and electricity generation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigator Series


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...