Multiple ion isolation and accumulation events for selective chemical noise reduction and dynamic range enhancement in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry†
Abstract
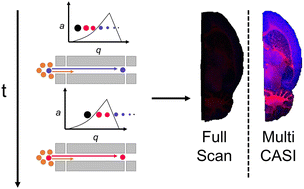
Abundant chemical noise in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry experiments can impede the detection of less abundant compounds of interest. This chemical noise commonly originates from the MALDI matrix as well as other endogenous compounds present in high concentrations and/or with high ionization efficiencies. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry of biological tissues measures numerous biomolecular compounds that exist in a wide range of concentrations in vivo. When ion trapping instruments are used, highly abundant ions can dominate the charge capacity and lead to space charge effects that hinder the dynamic range and detection of lowly abundant compounds of interest. Gas-phase fractionation has been previously utilized in mass spectrometry to isolate and enrich target analytes. Herein, we have characterized the use of multiple continuous accumulations of selected ions (Multi CASI) to reduce the abundance of chemical noise and diminish the effects of space charge in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry experiments. Multi CASI utilizes the mass-resolving capability of a quadrupole mass filter to perform multiple sequential ion isolation events prior to a single mass analysis of the combined ion population. Multi CASI was used to improve metabolite and lipid detection in the MALDI imaging mass spectrometry analysis of rat brain tissue.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 150th Anniversary Collection: Mass Spectrometry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...