A high-spin alkylperoxo–iron(iii) complex with cis-anionic ligands: implications for the superoxide reductase mechanism†
Abstract
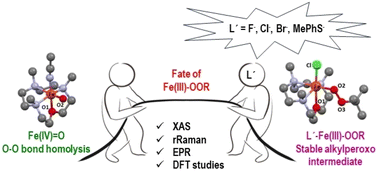
The N3O macrocycle of the 12-TMCO ligand stabilizes a high spin (S = 5/2) [FeIII(12-TMCO)(OOtBu)Cl]+ (3-Cl) species in the reaction of [FeII(12-TMCO)(OTf)2] (1-(OTf)2) with tert-butylhydroperoxide (tBuOOH) in the presence of tetraethylammonium chloride (NEt4Cl) in acetonitrile at −20 °C. In the absence of NEt4Cl the oxo–iron(IV) complex 2 [FeIV(12-TMCO)(O)(CH3CN)]2+ is formed, which can be further converted to 3-Cl by adding NEt4Cl and tBuOOH. The role of the cis-chloride ligand in the stabilization of the FeIII–OOtBu moiety can be extended to other anions including the thiolate ligand relevant to the enzyme superoxide reductase (SOR). The present study underlines the importance of subtle electronic changes and secondary interactions in the stability of the biologically relevant metal–dioxygen intermediates. It also provides some rationale for the dramatically different outcomes of the chemistry of iron(III)peroxy intermediates formed in the catalytic cycles of SOR (Fe–O cleavage) and cytochrome P450 (O–O bond lysis) in similar N4S coordination environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...