Magnetic carbon gate electrodes for the development of electrolyte-gated organic field effect transistor bio-sensing platforms†
Abstract
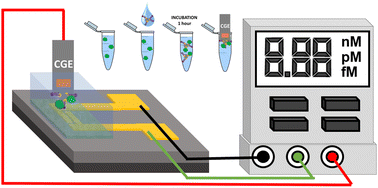
Electrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistors (EGOFETs) are promising devices for the development of bio-sensors. Typically, a gold gate electrode is functionalised with a self-assembled monolayer bearing the bio-receptor. Here, we propose a new route to fabricate EGOFET sensors using magnetic carbon-paste gate electrodes. In this way, magnetic nanoparticles properly modified with a bio-receptor are incubated with the analyte and, subsequently, collected on the gate electrode surface. Remarkably, these electrodes can be polished and re-used after each measurement. The feasibility of this route is here demonstrated for the biotin–avidin/streptavidin supramolecular complexes. High sensitivities and low limits of detection of the order of fM are achieved. Hence, this work demonstrates a novel and versatile strategy to exploit EGOFETs as sensing platforms.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In memory of Professor Gilles Horowitz


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...