Polymyxin B stabilized DNA micelles for sustained antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against P. aeruginosa†
Abstract
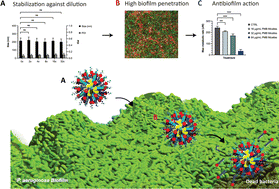
Nucleic acid-based materials showcase an increasing potential for antimicrobial drug delivery. Although numerous reports on drug-loaded DNA nanoparticles outline their pivotal antibacterial activities, their potential as drug delivery systems against bacterial biofilms awaits further studies. Among different oligonucleotide structures, micellar nanocarriers derived from amphiphilic DNA strands are of particular interest due to their spontaneous self-assembly and high biocompatibility. However, their clinical use is hampered by structural instability upon cation depletion. In this work, we used a cationic amphiphilic antibiotic (polymyxin B) to stabilize DNA micelles destined to penetrate P. aeruginosa biofilms and exhibit antibacterial/antibiofilm properties. Our study highlights how the strong affinity of this antibiotic enhances the stability of the micelles and confirms that antibacterial activity of the novel micelles remains intact. Additionally, we show that PMB micelles can penetrate P. aeruginosa biofilms and impact their metabolic activity. Finally, PMB micelles were highly safe and biocompatible, highlighting their possible application against P. aeruginosa biofilm-colonized skin wounds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...