Remarkable iodine uptake by aniline-based macrocyclic arenes through a reverse dissolution mechanism†
Abstract
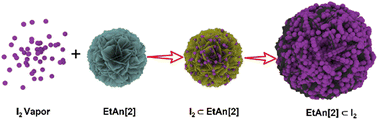
A series of aniline-based macrocycles (An[2]s) were synthesized and applied to iodine capture. The An[2]s showed remarkable iodine uptake capacities of up to 7.35 g g−1 in the vapor phase and significantly fast adsorption kinetics in both vapor and aqueous solutions. A new mechanism called reverse dissolution was proposed based on the unusually high iodine-loading capacities and the crystal-to-amorphous phase transition properties. The adsorbed iodine could be readily released by heating or immersing in an organic solvent, with the high iodine capture performance being kept after many cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...