Tunable thiophene-based conjugated microporous polymers for the disposal of toxic hexavalent chromium†
Abstract
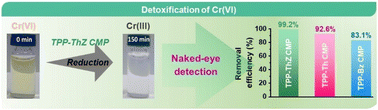
Herein we report the rational syntheses of three conjugated microporous polymers (CMPs) through one-pot polycondensation coupling of a boronated triphenylpyridine (TPP-3Bor) with 4,7-bis(5-bromothien-2-yl)benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole (ThZ-2Br), 2,5-dibromothiophene (Th-2Br), and 1,4-dibromobenzene (Bz-2Br), yielding the TPP-ThZ, TPP-Th, and TPP-Bz CMPs, respectively, featuring different thiophene contents, topologies, and molecular structures. Various characterization techniques are used to investigate the structural properties of these TPP-based CMPs, revealing their spherical morphologies, tunable pore volumes, and high thermal and chemical stabilities. We test the TPP-based CMPs for their use in the dynamic adsorptive reduction of toxic Cr(VI) ions. Among them, the TPP-ThZ CMP possesses the highest adsorption capacity for Cr(VI) (209 mg g−1); this performance is also higher than those of other recently reported adsorbents. Furthermore, our TPP-based CMPs exhibit good reusability for the reduction and adsorption of Cr(VI) ions. Accordingly, these novel thiophene-based CMPs not only function as dynamic materials for the reduction–adsorption of Cr(VI) but also reveal the potential of thiophene linkers in the future design of such Cr(VI) adsorbents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...