Highly selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction via a lead-free perovskite/MOF catalyst†
Abstract
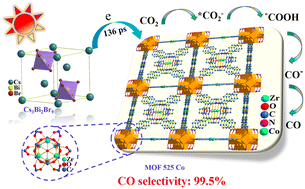
Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 in the atmosphere to fuels and value-added chemicals is a promising artificial carbon cycle to combat the global climate crisis, the accomplishment of which however is strongly reliant on efficient catalysts, i.e., with high selectivity, conversion rate, and robustness. In this work, we provide a solution involving the fabrication of a lead-free perovskite Cs3Bi2Br9/MOF 525 Co structure, where narrow band Cs3Bi2Br9 QDs for efficient light trapping and selective CO2 adsorption, coupled with MOF to form a Cs3Bi2Br9/MOF 525 Co type-II heterojunction for efficient electron–hole separation. In this way, three crucial steps, comprising light absorption, carrier transportation, and highly selective surface catalysis, were fully taken into account and the photocatalyst showed a high CO selectivity of 99.5% and an outstanding electron consumption rate of 124.8 μmol g−1 h−1 (61.2 μmol g−1 h−1 for CO, and 0.3 μmol g−1 h−1 for CH4) superior to previous reports. Femtosecond transient absorption measurements disclosed an ultrafast electron transfer of 136 ps from Cs3Bi2Br9 to MOF 525 Co within the heterojunction, enabling efficient charge separation with a long carrier life time over the ns time scale; further, in situ infrared measurements unraveled the stronger CO2 adsorption, efficient conversion to *COOH intermediates, and prompt CO desorption of the photocatalyst. The present work thus elucidated the underlying mechanism accounting for the high product selectivity, providing guidelines for the design of efficient catalysts from the perspective of dynamics and surface reaction activity.
- This article is part of the themed collections: #MyFirstJMCA and Photofunctional Materials and Transformations


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...