Effect of the polar group content on the glass transition temperature of ROMP copolymers†
Abstract
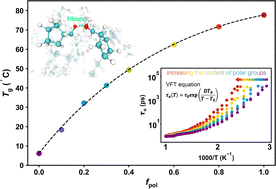
Polar groups have long been recognized to greatly influence the glass transition temperature (Tg) of polymers, but understanding the underlying physical mechanism remains a challenge. Here, we study the glass formation of ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) copolymers containing polar groups by employing all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. We show that although the number of hydrogen bonds (NHB) and the cohesive energy density increase linearly as the content of polar groups (fpol) increases, the Tg of ROMP copolymers increases with the increase of fpol in a nonlinear fashion, and tends to plateau for sufficiently high fpol. Importantly, we find that the increase rate of Gibbs free energy for HB breaking gradually slows down with the increase of fpol, indicating that the HB is gradually stabilized. Therefore, Tg is jointly determined by NHB and the strength of HBs in the system, while the latter dominates. Although NHB increases linearly with increasing fpol, the HB strength increases slowly with increasing fpol, which leads to a decreasing rate of increase in Tg.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...