Sustainable production of styrene from catalytic recycling of polystyrene over potassium promoted Fe–Al2O3 catalyst†
Abstract
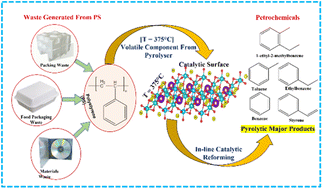
Used polystyrene is a part of the global plastic waste problem, which is increasing daily. A few million metric tons of EPS are produced each year, most for the packaging industry, and discarded after use. Therefore, the catalytic degradation of EPS into styrene was comprehensively studied over solid acid–base catalysts. Partial combinations of acids and bases have been used for enhanced liquid distillates and styrene selectivity. In this study, we report an alkali metal-supported Fe/γ-Al2O3 catalyst for the selective depolymerisation of polystyrene. It was found that the solid base catalyst (KFe/γ-Al2O3) was more effective with 83.2% styrene selectivity and ∼83% liquid yield. The facile physical adsorption of polystyrene molecules on the iron oxide surface and the controlled dissociation plays a vital role in suppressing the secondary products. The catalyst showed prolonged activity and stability; the catalyst was regeneratable for multiple cycles. The kinetic study proposed activation energies of 152.32 kJ mol−1 and 14.33 kJ mol−1 for thermal pyrolysis and catalytic depolymerisation, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...