Catenane formation of a cyclic poly(alkyl sorbate) via chain-growth polymerization induced by an N-heterocyclic carbene and ring-closing without extreme dilution†
Abstract
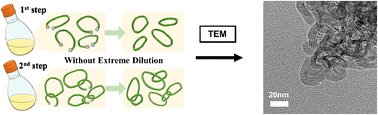
1,3-Di-tert-butylimidazol-2-ylidene (NHCtBu), a typical N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC), was previously found to induce the anionic chain-growth polymerization of ethyl sorbate (ES) in the presence of an aluminum Lewis acid, i.e., methylaluminum bis(2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenoxide) (MAD), in which the neighboring of α-terminal dienolate with a propagating anion induced cyclization without highly diluted conditions, after monomer depletion, to give the cyclic poly(ES). In this paper, we report that catenane formation occurs by two-step polymerization of ethyl sorbate (ES), in which, after complete monomer (ES) consumption ([ES]0/[NHCtBu]0 = 100/1) in toluene followed by purification by reprecipitation, a second addition of ES monomer ([ES]0/[ NHCtBu]0 = 20/1) in another pot (in toluene or tetrahydrofuran (THF)) resulted in catenane formation, namely a polycatenane. TEM images of a sample from the second step polymerization in THF revealed particles of polycatenane structure consisting of cyclic poly(ES) with sizes ranging from 200 to 1000 nm, showing that this NHCtBu triggered chain polymerization and successive cyclization without highly diluted conditions enabled us to fabricate the intended polycatenane in the successive two-step polymerization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...