Microstructure-driven electrical conductivity optimization in additively manufactured microscale copper interconnects†
Abstract
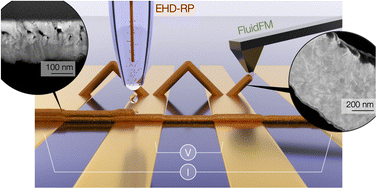
As the microelectronics field pushes to increase device density through downscaling component dimensions, various novel micro- and nano-scale additive manufacturing technologies have emerged to expand the small scale design space. These techniques offer unprecedented freedom in designing 3D circuitry but have not yet delivered device-grade materials. To highlight the complex role of processing on the quality and microstructure of AM metals, we report the electrical properties of micrometer-scale copper interconnects fabricated by Fluid Force Microscopy (FluidFM) and Electrohydrodynamic-Redox Printing (EHD-RP). Using a thin film-based 4-terminal testing chip developed for the scope of this study, the electrical resistance of as-printed metals is directly related to print strategies and the specific morphological and microstructural features. Notably, the chip requires direct synthesis of conductive structures on an insulating substrate, which is shown for the first time in the case of FluidFM. Finally, we demonstrate the unique ability of EHD-RP to tune the materials resistivity by one order of magnitude solely through printing voltage. Through its novel electrical characterization approach, this study offers unique insight into the electrical properties of micro- and submicrometer-sized copper interconnects and steps towards a deeper understanding of micro AM metal properties for advanced electronics applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...