Adsorptive removal of antibiotic pollutants from wastewater using biomass/biochar-based adsorbents
Abstract
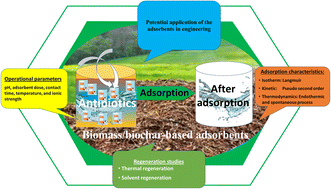
This study explores adsorptive removal measures to shed light on current water treatment innovations for kinetic/isotherm models and their applications to antibiotic pollutants using a broad range of biomass-based adsorbents. The structure, classifications, sources, distribution, and different techniques for the remediation of antibiotics are discussed. Unlike previous studies, a wide range of adsorbents are covered and adsorption of comprehensive classes of antibiotics onto biomass/biochar-based adsorbents are categorized as β-lactam, fluoroquinolone, sulfonamide, tetracycline, macrolides, chloramphenicol, antiseptic additives, glycosamides, reductase inhibitors, and multiple antibiotic systems. This allows for an assessment of their performance and an understanding of current research breakthroughs in applying various adsorbent materials for antibiotic removal. Distinct from other studies in the field, the theoretical basis of different isotherm and kinetics models and the corresponding experimental insights into their applications to antibiotics are discussed extensively, thereby identifying the associated strengths, limitations, and efficacy of kinetics and isotherms for describing the performances of the adsorbents. In addition, we explore the regeneration of adsorbents and the potential applications of the adsorbents in engineering. Lastly, scholars will be able to grasp the present resources employed and the future necessities for antibiotic wastewater remediation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2023 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...