Synthesis and biological activity of photostable and persistent abscisic acid analogs†
Abstract
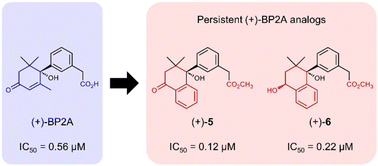
The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays a critical role in various environmental stress responses and has long been expected to be used in agriculture. However, the practical use of ABA has been limited, mainly because of its photoinstability and rapid biodegradation. We previously developed photostable ABA agonists, BP2A and Me 1′,4′-trans-diol BP2A, in which the dienoic acid side chain of ABA was replaced with phenylacetic acid. This finding validated our structure-based approach in designing photostable agonists and provided a basis for developing a more potent or long-lasting ABA agonist. In this study, we synthesized novel BP2A analogs in which the cyclohexenone ring was modified to avoid catabolism by the ABA metabolic enzyme, ABA 8′-hydroxylase. All synthesized analogs showed higher photostability than BP2A under sunlight. In an Arabidopsis seed germination assay, (+)-compounds 5 and 6 with a tetralone ring displayed significantly stronger ABA agonist activity than (+)-BP2A. In contrast, in the in vitro phosphatase assays, both compounds showed comparable or weaker ABA receptor (PYL1) agonistic activity than (+)-BP2A, suggesting that the stronger ABA-like activity of (+)-5 and (+)-6 may arise from their metabolic stability in vivo. This study provides data relevant to designing photostable and persistent ABA agonists.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...