Defining the substrate scope of DNAzyme catalysis for reductive amination with aliphatic amines†
Abstract
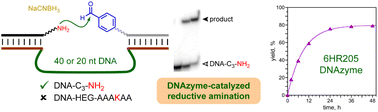
Amines can be alkylated using various reactions, such as reductive amination of aldehydes. In this study, we sought DNAzymes as catalytic DNA sequences that promote reductive amination with aliphatic amines, including DNA-anchored peptide substrates with lysine residues. By in vitro selection starting with either N40 or N20 random DNA pools, we identified many DNAzymes that catalyze reductive amination between the DNA oligonucleotide-anchored aliphatic amino group of DNA-C3-NH2 (C3 = short three-carbon tether) and a DNA-anchored benzaldehyde group in the presence of NaCNBH3 as reducing agent. At pH 5.2, 6.0, 7.5, or 9.0 in the presence of various divalent metal ion cofactors including Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+ and Ni2+, the DNAzymes have kobs up to 0.12 h−1 and up to 130-fold rate enhancement relative to the DNA-splinted but uncatalyzed background reaction. However, analogous selection experiments did not lead to any DNAzymes that function with DNA-HEG-NH2 [HEG = long hexa(ethylene glycol) tether], or with short- and long-tethered DNA-AAAKAA and DNA-HEG-AAAKAA lysine-containing hexapeptide substrates (A = alanine, K = lysine). Including a variety of other amino acids in place of the neighboring alanines also did not lead to DNAzymes. These findings establish a practical limit on the substrate scope of DNAzyme catalysis for N-alkylation of aliphatic amines by reductive amination. The lack of DNAzymes for reductive amination with any substrate more structurally complex than DNA-C3-NH2 is likely related to the challenge in binding and spatially organizing those other substrates. Because other reactions such as aliphatic amine N-acylation are feasible for DNAzymes with DNA-anchored peptides, our findings show that the ability to identify DNAzymes depends strongly on both the investigated reaction and the composition of the substrate.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating the 20th anniversary of Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...