Bubble-propelled micromotors for ammonia generation†
Abstract
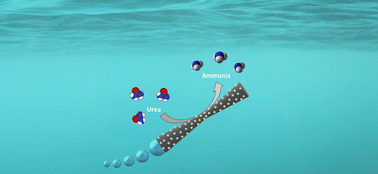
Micromotors have emerged as promising tools for environmental remediation, thanks to their ability to autonomously navigate and perform specific tasks at the microscale. In this study, we present the development of MnO2 tubular micromotors modified with laccase for enhanced oxidation of organic pollutants by providing an additional oxidative catalytic pathway for pollutant removal. These modified micromotors exhibit efficient ammonia generation through the catalytic decomposition of urea, suggesting their potential application in the field of green energy generation. Compared to bare micromotors, the MnO2 micromotors modified with laccase exhibit a 20% increase in rhodamine B degradation. Moreover, the generation of ammonia increased from 2 to 31 ppm in only 15 min, evidencing their high catalytic activity. To enable precise tracking of the micromotors and measurement of their speed, a deep-learning-based tracking system was developed. Overall, this work expands the potential applicability of bio-catalytic tubular micromotors in the energy field.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Micro- and nano-motors, Celebrating International Women’s day 2024: Women in Nanoscience and Nanoscale Most Popular 2023 Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...