New reagents for selective extraction of Pd(ii) and Au(iii) from acidic media†
Abstract
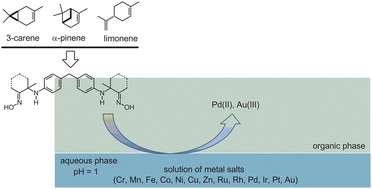
A series of novel terpene-based reagents are investigated as potential molecules for the liquid–liquid extraction of noble metals from chloride solutions. The chemical structures of new promising extractants include a chelator of the bis(α-amine oxime) type embedded in a monoterpene environment. Chelating groups embedded in the terpene framework are capable of forming quite stable complexes with increased lipophilicity, which is important for extraction in a liquid–liquid system when using aqueous solutions of metal salts and organic solvents. The nature of the monoterpene framework plays a minor role, and derivatives of different terpenes (3-carene, α-pinene and limonene) with the same chelating moiety demonstrate similar properties. The new extractants demonstrate remarkable selectivity in the extraction of Pd(II) from complex mixtures containing d-block elements (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn). With the simultaneous presence of noble metals in an aqueous solution, the molecules studied extracted only Pd(II) and Au(III), while Ru(III), Rh(III), Ir(III) and Pt(IV) remain completely in the aqueous phase. From mixtures of 3d-elements and noble metals, only Pd(II) and Au(III) are extracted, and the total quantity and composition of the 3d-element mixture have some effect on the degree of Au(III) recovery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...