Prediction of dissolution profiles of sinomenine hydrochloride sustained-release tablets part I: using near-infrared spectra as predictors†
Abstract
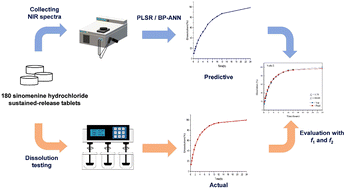
The objective of this study was to verify the feasibility of the prediction of in vitro dissolution profiles using near-infrared spectroscopy as a technical means, taking the prepared sinomenine hydrochloride (SH) sustained-release tablets as an example. In this work, N = 36 batches of representative SH sustained-release tablets were prepared with a D-optimal design, and the near infrared spectra were collected. Dissolution profiles were then obtained using the USP Apparatus II method (paddle method). The dissolution rates of each sample were correlated with the NIR spectra of five tablets from each batch, using the partial least squares regression (PLSR) algorithm and the back-propagation artificial neural network (BP-ANN) algorithm, to establish the calibration models. The established models were validated with a test set, and the difference factor f1 and the similarity factor f2 between the measured and predicted curves were calculated to evaluate the prediction accuracy. The prediction results of the BP-ANN and PLSR models were compared with the measured dissolution profiles, and the results demonstrated that the optimized PLSR model could predict the dissolution profiles accurately: with R2 greater than 0.95 and RMSEP of 5.9111%. This model was used to predict the dissolution profiles of the validation set and the result of the prediction accuracy was 96%. The fitted dissolution equation parameters of the dissolution curves were tested using the paired t-test, and the p values were greater than 0.05, which indicated that there was no significant difference between the predicted and fitted dissolution equation parameters at the 95% confidence interval. In summary, the established method based on NIR spectroscopy can predict the dissolution behavior of SH sustained-release tablets effectively. Therefore, NIR spectroscopy combined with chemometrics has great potential in the dissolution test for oral solid dosages.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...