In situ formation of biocompatible and ductile protein-based hydrogels via Michael addition reaction and visible light crosslinking†
Abstract
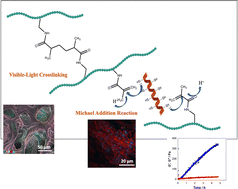
Keratin, a biological polymer with high sulfur content, is the main component of hair, feathers and wool. Human hair is the cheapest natural source of keratin. In this study, an optimized and very effective reduction reaction method was used to obtain keratin from human hair. During this process, the disulfide bridge of keratin was reduced in the presence of sodium sulfide to form free sulfhydryl (thiols) that would act as a strong nucleophile. The results of FTIR spectroscopy, Tricine-SDS-PAGE and MALDI-TOF/MS verified the successful extraction of the reduced human hair keratin. A well-interconnected structure with three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds was prepared using keratin and methacrylated gelatin (GelMA), KeratinGel, for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. KeratinGel hydrogels were in situ prepared via Michael addition reaction and visible light crosslinking. Two complementary crosslinking reactions were combined to enhance the network structure and provide ductility. With the targeted two-step method, the reactivity of vinyl groups of GelMA to photocrosslinking and thiol groups in keratin to the Michael addition reaction was exploited. Rheological monitoring of the Michael addition reaction was performed for KeratinGel hydrogels in a basic reaction environment at pH 7.4 with a constant concentration of GelMA (10% w/v) and different amounts of reduced human hair keratin (5, 7.5 and 10% w/v) at room temperature. The physical properties, swelling and degradation rates of KeratinGel hydrogels were determined to understand their suitability for tissue regeneration. We finalize that KeratinGel hydrogels would be better in minimally invasive surgeries, soft tissue engineering, especially with in situ gelling features, and favourable for the preparation of complex shapes and applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...