A palladium nanoparticle implanted polymer membrane for reusable dip-catalysis of diverse C–C and C–heteroatom (O/S/N) coupling reactions†
Abstract
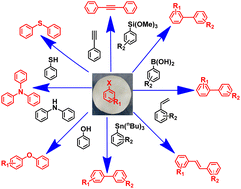
The criteria for the development of a successful catalyst are simple yet cheap fabrication, high efficiency, stability, flexibility, straightforward recovery, reusability, and ease of scale-up. There are reports of palladium nanoparticle (PdNP)-based catalysts for performing carbon–carbon cross-coupling reactions, but the aforesaid criteria are rarely met in a single system. Moreover, a single catalyst system performing different types of C–C and C–heteroatom cross-coupling reactions is very rare. Herein, we achieved the above-mentioned criteria by using a reusable polymer-embedded Pd nanoparticle dip-catalyst membrane without any other ligands or additives under milder reaction conditions. The composite membrane was fabricated by simply depositing poly(4-vinyl pyridine) anchored PdNPs (average size 9.9 nm) onto a nylon-6 membrane followed by UV cross-linking. C–C bond formation reactions using diverse reagents (Suzuki–Miyaura, Heck, Sonogashira, Stille, Hiyama reactions) were achieved to give the desired products in high to excellent isolated yields, while C–X (X = N/O/S) bond formations were accomplished in moderate to good isolated yields. The turnover number (TON) and frequency (TOF) for the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction are calculated as ≥×104 and 3.11 s−1, respectively. The P4VP–PdNP dip-catalyst system was stable under the reaction conditions without significant leaching of Pd into the solution. The dip-catalyst membrane can be reused at least 10 times without losing any significant activity. The substrate scope for most of the cross-coupling reactions was tested, which indicates functional group tolerance and that the coupling reaction can take place with moieties having electron donating or withdrawing groups.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...