Low temperature in situ immobilization of nanoscale fcc and hcp polymorphic nickel particles in polymer-derived Si–C–O–N(H) to promote electrocatalytic water oxidation in alkaline media†
Abstract
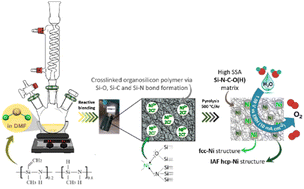
We synthesized nickel (Ni) nanoparticles (NPs) in a high specific surface area (SSA) p-block element-containing inorganic compound prepared via the polymer-derived ceramics (PDC) route to dispatch the obtained nanocomposite towards oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The in situ formation of Ni NPs in an amorphous silicon carboxynitride (Si–C–O–N(H)) matrix is allowed by the reactive blending of a polysilazane, NiCl2 and DMF followed by the subsequent thermolysis of the Ni : organosilicon polymer coordination complex at a temperature as low as 500 °C in flowing argon. The final nanocomposite displays a BET SSA as high as 311 m2 g−1 while the structure of the NPs corresponds to face-centred cubic (fcc) Ni along with interstitial-atom free (IAF) hexagonal close-packed (hcp) Ni as revealed by XRD. A closer look into the compound through FEG-SEM microscopy confirms the formation of pure metallic Ni, while HR-TEM imaging reveals the occurrence of Ni particles featuring a fcc phase and surrounded by carbon layers; thus, forming core–shell structures, along with Ni NPs in an IAF hcp phase. By considering that this newly synthesized material contains only Ni without doping (e.g., Fe) with a low mass loading (0.15 mg cm−2), it shows promising OER performances with an overpotential as low as 360 mV at 10 mA cm−2 according to the high SSA matrix, the presence of the IAF hcp Ni NPs and the development of core–shell structures. Given the simplicity, the flexibility, and the low cost of the proposed synthesis approach, this work opens the doors towards a new family of very active and stable high SSA nanocomposites made by the PDC route containing well dispersed and accessible non-noble transition metals for electrocatalysis applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...