3D-printed polymer composite devices based on a ferroelectric chiral ammonium salt for high-performance piezoelectric energy harvesting†
Abstract
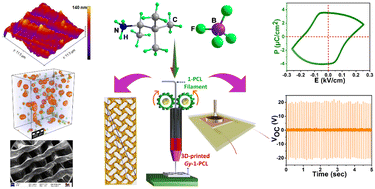
Three-dimensional printing (3DP) is an emerging technology to fabricate complex architectures, necessary to realize state-of-the-art flexible and wearable electronic devices. In this regard, top-performing devices containing organic ferro- and piezoelectric compounds are desired to circumvent significant shortcomings of conventional piezoceramics, e.g. toxicity and high-temperature device processibility. Herein, we report on a 3D-printed composite of a chiral ferroelectric organic salt {[Me3CCH(Me)NH3][BF4]} (1) with a biodegradable polycaprolactone (PCL) polymer that serves as a highly efficient piezoelectric nanogenerator (PENG). The ferroelectric property of 1 originates from its polar tetragonal space group P42, verified by P–E loop measurements. The ferroelectric domain characteristics of 1 were further probed by piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM), which gave characteristic ‘butterfly’ and hysteresis loops. The PFM amplitude vs. drive voltage measurements gave a relatively high magnitude of the converse piezoelectric coefficient for 1. PCL polymer composites with various weight percentages (wt%) of 1 were prepared and subjected to piezoelectric energy harvesting tests, which gave a maximum open-circuit voltage of 36.2 V and a power density of 48.1 μW cm−2 for the 10 wt% 1-PCL champion device. Furthermore, a gyroid-shaped 3D-printed 10 wt% 1-PCL composite was fabricated to test its practical utility, which gave an excellent output voltage of 41 V and a power density of 56.8 μW cm−2. These studies promise the potential of simple organic compounds for building PENG devices using advanced manufacturing technologies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...