Physicochemical properties, phenolic content and in vitro digestion profile of Chinese black rice (Oryza sativa L.)†
Abstract
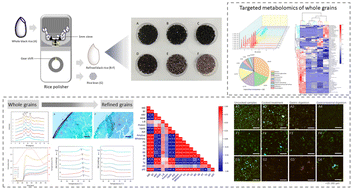
Yangxian black rice, as one of the ancient Chinese black rice varieties, is widely planted in the Yangxian area of China. This study investigated the physicochemical properties, phenolic content and in vitro digestion profile of Chinese black rice under gradient milling treatment. The chemical composition, color, pasting and thermal properties of black rice with different milling degrees were comprehensively compared. In vitro digestion analysis indicated that cooked rice flour had higher rapidly digestible starch (RDS) and lower resistant starch (RS) contents compared with the uncooked one. Besides, all cooked black rice samples exhibited high predicted glycemic index (pGI) value and whole black rice showed a lower pGI than refined rice. The microstructure and the abundance of phenolic compounds in the solid matrix during different treatments or digestion stages were observed by CLSM. Furthermore, a total of 102 phenolic constituents were absolutely quantified by targeted metabolomics techniques. Methanol extraction and moderate cooking treatment contributed to the release of phenolic compounds from the solid matrix of whole black rice. Besides, compared to the gastric digestion stage, the transition in the intestinal environment caused a decrease in the majority of the analyzed polyphenols. Identifying the phenolic constituents was favorable for a better elucidation of the chemical basis of the function and nutritional value of Chinese black rice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...